VIAVI OTDR
Electro Rent partners with VIAVI to provide innovative ways for customers to access intuitive, easy-to-use test solutions for complex 5G and fiber networks. We provide rental and financial solutions that are customized for your unique project requirements.
Featured VIAVI OTDR
Frequently Asked Questions
OTDRs
OTDRs are a class of instruments that perform an optical time-domain reflectometry test on a fiber optic cable. OTDRs 'shoot' a fiber optic cable with a light pulse, then look at the returned light as reflections. An OTDR trace signal can identify places where there are issues with a fiberoptic cable. Traces are a graph of the reflections from the initial light pulse represented in light power in dB. Reflected power is often reported in negative dB. The larger the negative number, less light is being reflected.
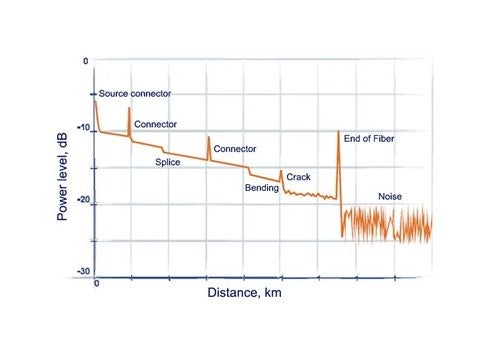
Reflections represent areas of fiber that could have issues or problems that need to be addressed. The OTDR also measures the time that the reflected light takes to arrive back at the OTDR. In this way the OTDR can tell the user where along the fiber to look for the problems.
Testing Using an OTDR
OTDRs work by injecting optical pulses into the fiber under test and measuring the light that is reflected from various points along the fiber. The reflected light is used to characterize the fiber under test with the strength of the return pulses being integrated against time and plotted as a function of fiber length. By using an OTDR at various points in the network, the feeder and distribution sections of the network can be tested independently. The OTDR can identify and locate each network component and can measure splice loss, connector loss, and reflectance along with total end-to-end loss and optical return loss (ORL). The tests must be performed using two wavelengths, enabling detection of bends on the link, which give higher losses at 1550 nm than at 1310 nm. In addition to using the OTDR as a qualification tool, it can also be used as a troubleshooting tool to pinpoint issues along the link.
OTDR features like accuracy, resolution, measurement range, and measurement speed vary according to their performance, and there are a wide range of OTDR models on the market, each addressing different test and measurement and performance needs. The suitability of an OTDR for a specific test scenario depends on several factors, including type of network, type of fiber (singlemode or multimode), maximum test distance, and test types. Other factors to consider include size and weight, display size, battery life, data storage, connectivity, post-processing software, and available upgrade modules.
What types of fiber do OTDRs test?
There are two main types of fiber, singlemode (SM) and multimode (MM). Multimode fiber is used for short distances, but has a larger diameter and light reflects off the walls creating modes. Single mode fiber has a smaller diameter and is used for distances greater than 50m. Light in a singlemode fiber travels the distance of the fiber without reflecting off the walls of the fiber.
| Singlemode (SM) | Wavelength | Notes |
| 1310 & 1550 nm | Primary wavelengths used in SM OTDR measurements | |
| 1625 & 1650 nm | Used in troubleshooting when testing on active networks | |
| 1310, 1550, 1625 nm | Should be used to future-proof all new construction builds | |
CWDM - Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing 1270 to 1610 nm | CWDM is a technology that allows multiple light wavelengths to be transmitted over a single fiber at the same time. The OTDR needs to “tune” to a specific channel within the wavelength range. | |
DWDM - Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing 1530 to 1565 nm | DWDM is a technology like CDWM but contains ten times more channels and is therefore ‘denser’ |
| Multimode (MM) | Wavelength | Notes |
| 850, 1300 nm | Used when MM fiber is used for shorter distances in LANs and datacenters. | |
| 1300 nm | Used for longer distances in metropolitan applications like |
What are the important factors to consider when looking for a VIAVI OTDR?
Her are some considerations to help you select the ideal OTDR:
- Type of fiber under test: Look for a device that suits the type of fiber you plan to test. You may use single-mode fibers, multi-mode fibers, or both. Viavi also offers QUAD mode OTDRs that test both SM and MM fiber in four (1310, 1550, 850, 1300nm) wavelengths. QUAD OTDRs are good for testing both types of fibers.
- Dead zones: These zones are listed in meters at the shortest pulse width. In most applications, the shortest dead zone for the task is ideal. The dead zone represents a short distance from the OTDR that it cannot detect. This is overcome by the addition of launch cables by the user. A short length of fiber with the appropriate connectors allows the OTDR to see into nearby cable faults.
- Dynamic range: This range affects how far the device can measure. It is the measurement in dB that the longest pulse width reaches. Some devices have a display range or distance range to indicate the ability of the device. Keep in mind that display range differs from dynamic range. The length of fiber under test is important to consider with dynamic range. For example, a higher dynamic range is important for long-haul projects, but not necessary when testing shorter links.
Do you need help picking the right new or used VIAVI OTDR? Electro Rent partners with VIAVI and can help you find the right device. You can buy or rent VIAVI OTDR devices with set monthly payments, no money up-front, and no long-term commitments.






